
LastPass is warning customers of a phishing campaign sending emails with an access request to the password vault as part of a legacy inheritance process.
The activity started in mid-October, and the domains and infrastructure used point to a financially motivated threat group called CryptoChameleon (UNC5356).
CryptoChamemelon employs a phishing kit specializing in cryptocurrency theft, targeting multiple wallets including Binance, Coinbase, Kraken, and Gemini, using fake Okta, Gmail, iCloud, and Outlook sign-in pages.
LastPass users were targeted by the same group again in April 2024, but the newest campaign appears to be more extensive and also enhanced, now targeting passkeys too.
The phishing emails sent to LastPass users claim that a family member requested access to their LastPass vault by uploading a death certificate.
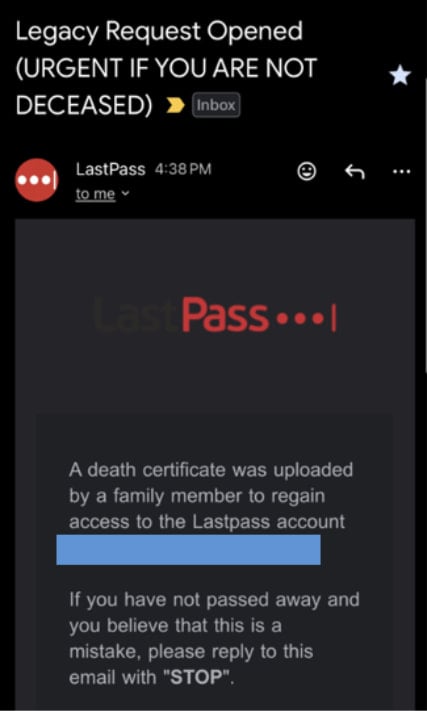 Phishing message sent by CryptoChameleon
Phishing message sent by CryptoChameleonSource: LastPass
LastPass’s inheritance process is an emergency access feature that allows individuals designated by account holders to request access to their vault in case of death or incapacity.
When such a request is opened, the account holder receives an email, and after a waiting period expires, access is automatically granted to the contact.
The fabricated legacy request includes an agent ID number for added legitimacy, prompting the recipient to take action and cancel it if they are not deceased by clicking a link.
However, the link redirects them to a fraudulent page on lastpassrecovery[.]com that features a login form where the victim can enter their master password.
LastPass says that in some cases the threat actor called victims posing as LastPass staff and directed them to enter their credentials on the phishing site.
The company says that one key element in the CryptoChameleon attack targeting its users is the use of passkey-focused phishing domains such as mypasskey[.]info and passkeysetup[.]com, which indicate attempts to steal users’ passkeys.
Passkeys are a passwordless authentication standard based on the FIDO2 / WebAuthn protocols, using assymmetric cryptography instead of memorized passwords.
Modern password managers like LastPass, 1Password, Dashlane, and Bitwarden now store and sync passkeys across devices, and threat actors have started to target them directly.
In 2022, LastPass suffered a major data breach where attackers stole encrypted vault backups. The incident was linked to targeted attacks that followed, resulting in losses of roughly $4.4 million in cryptocurrency.
.png)
 4 hours ago
1
4 hours ago
1





