A Fedora BootC OS themed like it's 2003, but updated like it's 2025.
A graphical, declarative OS with a retro theme (Bluecurve) reminiscent of Fedora Core 1.0.
Using bootc for transactional upgrades!
All built within only ONE FILE (Containerfile)!
This main OS image is hosted on Quay.io:
[1] Technically the /theme folder is passed in. Otherwise, everything is in a single Containerfile!
This Bootable Container (bootc) OS uses bootc-image-builder to produce bootable container disk images.
You will use this to add users so you can log in!
Once a machine is created from the disk image, it can apply transactional updates in place from newly pushed container images (no need to rebuild the disk image). After you push a new image (podman push), just run bootc upgrade on the system and reboot.
There are some default applications bundled into this OS in additional to the default Fedora images:
- Visual Studio Code (core)
- Laptop and server hardware support (core)
- WiFi hardware support (core)
- Container tools such as Podman (core)
- Wireguard support (core)
- Firefox (Flatpak)
- Podman Desktop (Flatpak)
If you want to learn more about bootable containers, see the Fedora Getting Started Guide for videos, demos, best practices and more details.
- To install additional software, use Flatpak.
- Want to install a package to the core of the OS? See Advanced Usage.
- ONLY generic GPU drivers are included (Intel iGPU, AMD iGPU, etc.) from @hardware-support in RHEL-derivative OSes.
- No NVIDIA GPU support yet (upcoming).
- No AMD GPU support yet (upcoming).
We have to initially build our OS! So look below for requirements.
OS:
Compatible on Windows, macOS & Linux.
Software:
-
Pull the container image:
Pull via CLI or within Podman Desktop
podman pull quay.io/blueboots/os -
(Alternatively) Build your own bootc-enabled Containerfile:
Git clone this project and build your image locally.
git clone http://github.com/bluebootsy/os podman build -t quay.io/foo/bar . -
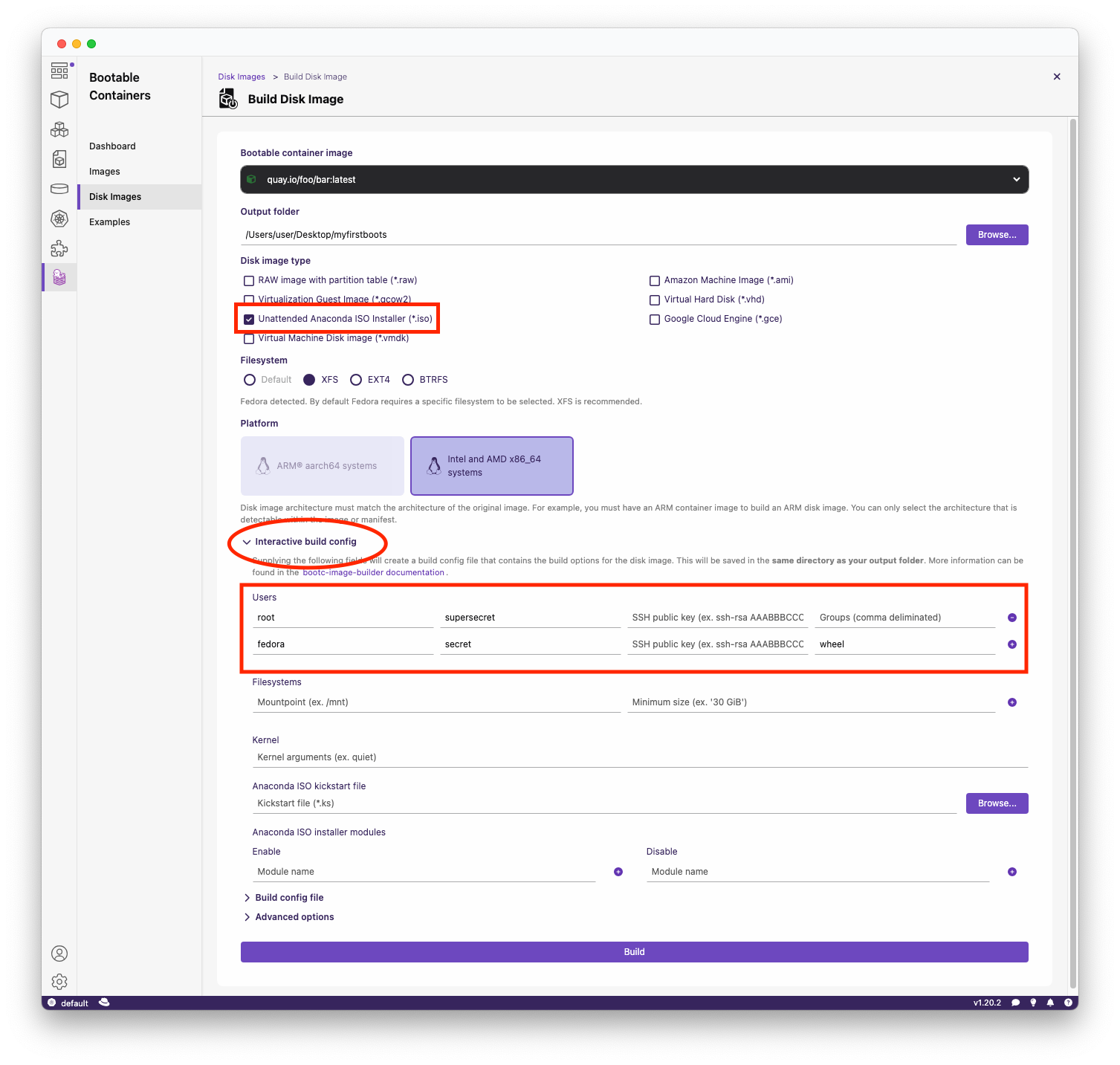
Build the disk image:
Use the Podman Desktop BootC extension. Make sure you provide your username and password.
Important note: Use the interactive installer within the BootC extension to add your username and password! Otherwise you will NOT BE ABLE TO LOGIN.
- Choose either .iso for an unattended ISO installer which will AUTOMATICALLY WIPE THE FIRST AVAILABLE DISK (use with caution!), or .raw/other image types for local testing (e.g. writing to a USB stick).
- Add your username and password for logging in, as well as your group (e.g. wheel for passwordless sudo).
LET ME REPEAT.
IF YOU CREATE THE .ISO, IT WILL AUTO-INSTALL TO YOUR FIRST AVAILABLE DISK AFTER SELECTING IT FOR BOOTING. -
Installation:
If you chose ISO:
- "Write" the ISO using balenaEtcher or Fedora Media Writer to a USB stick.
- Plug into a PC and select the USB from the boot screen.
- Watch as it installs unattended to the first available drive.
If you chose RAW:
- You can "write" the .raw image with the above tools (balenaEtcher or Fedora Media Writer) to a USB stick.
- Plug into a PC and select the USB from the boot screen.
- Test out the "live" image.
Want to change a "core" package or make system changes that propagate to your OS? Follow below!
Software that is consistently being upgraded should be installed as a Flatpak.
We recommend using Flathub as the main way of installing new software.
This can be done on the command line after your OS has booted:
In this example we will add a basic package called figlet:
-
Edit your Containerfile:
Within the Containerfile add the following to the list of packages:
RUN dnf install -y \ # ... other packages ... \ figlet && \ dnf clean all && \ rm -rf /var/cache/dnf -
Build & push your container:
podman build -t quay.io/foo/bar . podman push quay.io/foo/bar -
Run bootc upgrade on your OS:
The command downloads your hosted image and applies updates on next reboot.
-
Reboot and check that figlet is installed!
$ figlet "Hi" _ _ _ | | | (_) | |_| | | | _ | | |_| |_|_|
The bootc CLI is the bread-and-butter of bootc-derived images. Once booted, you can manage the system with:
- Status: bootc status shows the current image and version.
- Upgrade: bootc upgrade pulls the latest OCI image to apply next reboot.
- Fetch: bootc fetch pre-downloads an update without applying it.
- Install: bootc install --target /dev/sdX writes the OS to a block device (useful when live-booting from USB for testing).
See the official docs: https://bootc-dev.github.io/bootc
No GPU support for NVIDIA and AMD (yet).
.png)