A comprehensive guide comparing whey isolate and concentrate: protein content, digestibility, cost, and more
Decoding the Whey Protein Dilemma
Choosing between whey protein isolate and concentrate? This listicle breaks down the six key differences between whey isolate vs concentrate, helping you make the right choice for your fitness goals and budget. Understand how protein content, fat, carbs, digestibility, processing, and price compare. Whether you're a bodybuilder, health-conscious consumer, or on a special diet, this guide empowers you to choose the optimal whey.
1. Protein Content
When comparing whey isolate vs concentrate, the most significant difference lies in their protein content. This is the primary factor influencing other aspects like price, calorie content, and overall effectiveness. Whey isolate typically boasts a protein content of 90% or higher by weight, meaning that a 100g serving of whey isolate would contain at least 90g of pure protein. In contrast, whey concentrate usually contains between 70-80% protein by weight. This difference arises from the more rigorous filtration process whey isolate undergoes. This extensive filtration removes more of the non-protein components like fat, lactose, and carbohydrates, resulting in a purer protein product.
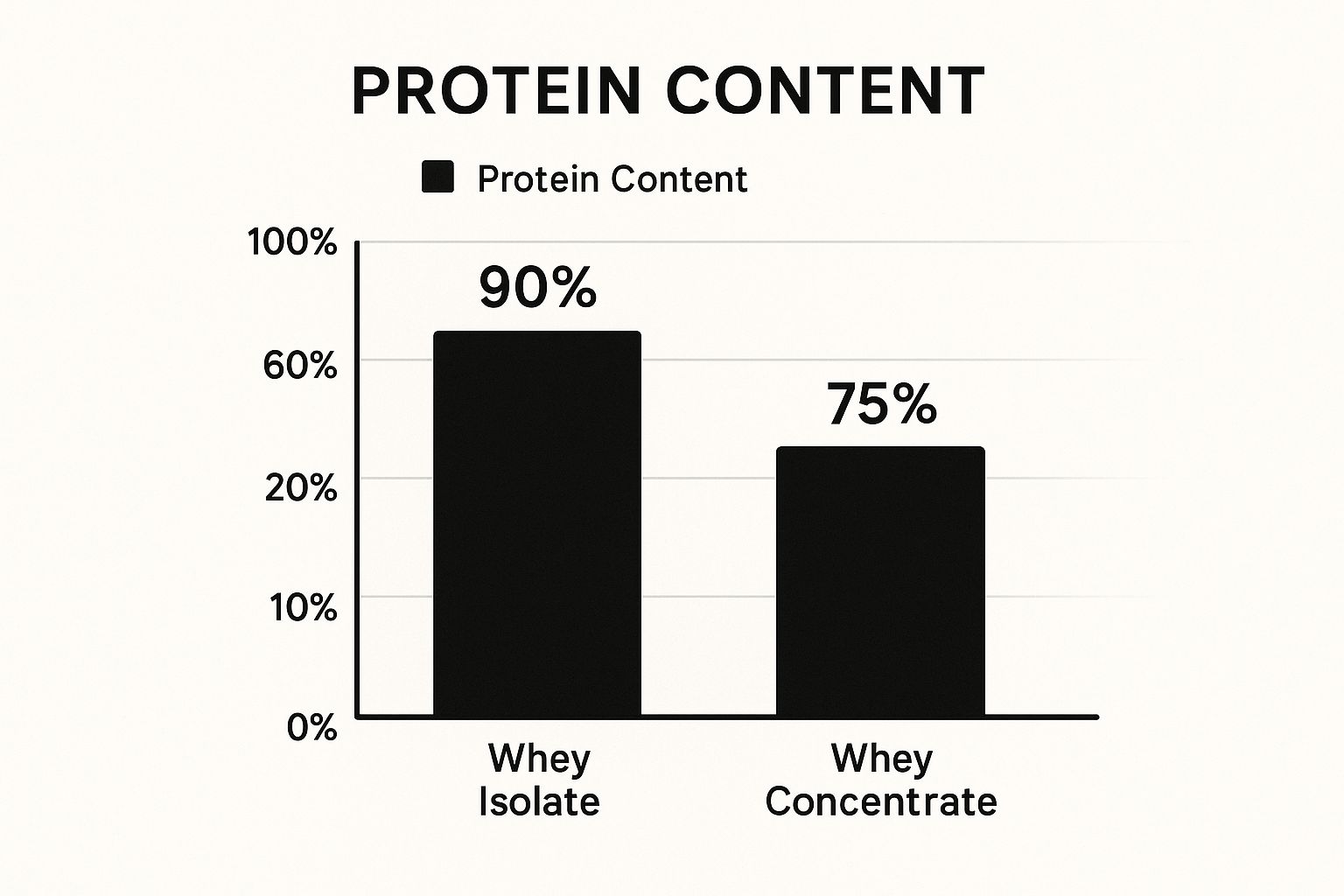
This bar chart clearly visualizes the difference in protein content between whey isolate and concentrate. As shown, isolate consistently sits above the 90% mark, while concentrate averages around 75%. This 15-20% difference is substantial and directly impacts the amount of protein you consume per serving.
This difference in protein concentration directly impacts how much protein you get per serving. For instance, Dymatize ISO100 (an isolate) packs 25g of protein into a 27g serving, whereas Optimum Nutrition Gold Standard Whey (a concentrate blend) provides 24g of protein in a 30g serving. This illustrates how you get more protein per gram with isolate. The higher protein percentage in isolate also translates to fewer calories from other sources, making it ideal for those watching their calorie intake. However, this increased purity comes at a price, making whey isolate generally more expensive than concentrate.
Learn more about Protein Content
Pros of Whey Isolate's Higher Protein Content:
-
More protein per gram: Maximize your protein intake with smaller serving sizes.
-
Fewer calories from other sources: Ideal for weight management and cutting phases.
Cons of Whey Isolate's Higher Protein Content:
- Higher cost: The more refined filtration process makes isolate more expensive.
When to Choose Whey Isolate vs. Concentrate:
-
Choose isolate: When prioritizing maximum protein intake with minimal calories, during cutting or leaning phases, or if you have lactose intolerance.
-
Choose concentrate: For a more budget-friendly option when absolute protein purity isn't essential, or when you prefer a slightly creamier texture and flavor.
Protein content is a crucial factor when deciding between whey isolate and concentrate. Understanding this difference allows you to choose the best whey protein to align with your individual fitness goals, dietary needs, and budget. This fundamental aspect of whey protein makes "Protein Content" a vital point of comparison in any discussion of "whey isolate vs concentrate," and deserves its place at the top of this list. Popularized by professional bodybuilders and sports nutrition companies like Dymatize and Isopure, focusing on protein content helps consumers make informed decisions about their supplement choices.
2. Fat and Carbohydrate Content
A key differentiator between whey protein isolate and concentrate lies in their fat and carbohydrate content. This difference stems from the filtration processes used in their production. Whey protein concentrate retains more of the original milk's composition, including fat and lactose (milk sugar). In contrast, whey isolate undergoes more intensive processing, such as microfiltration, ion-exchange, or cross-flow microfiltration, which removes a significant portion of these macronutrients. This results in a purer protein product with minimal fat and carbohydrates. Understanding this distinction is crucial for tailoring your protein supplement to your specific dietary needs and goals.
Typically, whey protein isolate contains less than 1% fat and less than 1% lactose. Whey concentrate, on the other hand, typically contains between 2-8% fat and 4-8% lactose. This makes whey isolate an ideal choice for individuals following low-carb or low-fat diets, as it provides fewer calories per gram of protein. For those meticulously tracking their macronutrient intake, or individuals with lactose intolerance, isolate offers a cleaner nutritional profile.
However, the additional processing of whey isolate can also be a drawback. While not as abundant as in concentrate, the fat in whey concentrate includes beneficial lipids. The processing used to create isolate can remove some of these potentially beneficial components, along with certain immune-boosting factors found in the original milk. Learn more about Fat and Carbohydrate Content This can be a consideration for individuals prioritizing whole-food sources and maximizing nutrient intake.
As a practical example, IsoPure Zero Carb, a popular isolate product, lives up to its name, containing 0g of carbohydrates per serving. Conversely, MusclePharm Combat Whey, a concentrate, contains 3g of carbs and 1.5g of fat per serving. These differences highlight the impact of processing on the final macronutrient composition.
When choosing between whey isolate vs concentrate, consider your individual goals and dietary restrictions. If you're cutting, on a calorie-restricted diet, or have lactose intolerance, whey isolate is generally the preferable choice. Conversely, during bulking phases when additional calories are desired, or if maximizing potential immune benefits is a priority, whey concentrate may be more beneficial. This fat and carbohydrate comparison earns its place in the isolate vs. concentrate debate because it directly impacts the nutritional value and suitability of each protein type for different dietary needs and fitness goals.
3. Digestibility and Lactose Content
A key difference between whey isolate and concentrate lies in their digestibility and lactose content, a crucial factor for many individuals. This distinction stems from the processing methods used to create each type of whey protein. Whey concentrate undergoes less filtration, retaining more of the original milk sugars (lactose). Whey isolate, on the other hand, undergoes a more extensive filtration process, removing a significant portion of these sugars. This difference has a direct impact on how easily the body processes each type of whey protein, making it an important consideration when choosing between whey isolate vs concentrate.
Typically, whey isolate contains less than 1% lactose, compared to 4-8% in whey concentrate. This dramatic reduction makes isolate a much more suitable choice for individuals with lactose sensitivity or intolerance. While concentrate may cause bloating, gas, and other digestive discomfort for these individuals, isolate generally minimizes these issues. For those seeking optimal comfort and efficient digestion, understanding the lactose content in whey isolate vs concentrate is paramount. Learn more about Digestibility and Lactose Content
Features:
-
Isolate: Typically <1% lactose
-
Concentrate: 4-8% lactose
-
Isolate: Causes fewer digestive issues for lactose-sensitive individuals
Pros:
-
Isolate is more easily digested by most people.
-
Isolate causes less bloating and digestive discomfort.
Cons:
- Some individuals with extreme lactose sensitivity may still react to the trace amounts of lactose in isolate.
Examples:
-
Dymatize ISO100 markets itself as "lactose-free," highlighting its appeal to lactose-sensitive consumers.
-
Many online reviews and forum discussions feature users reporting that switching from concentrate to isolate resolved their digestive issues.
Tips:
-
Start with whey protein isolate if you have any level of lactose sensitivity.
-
If you experience digestive issues with whey concentrate, try isolate before abandoning whey protein altogether.
This aspect of whey isolate vs concentrate is particularly important for athletes with lactose intolerance, fitness influencers promoting gut health, and brands specializing in easily digestible protein, such as Isopure and Dymatize. The digestibility and lactose content of whey protein directly affects user experience and overall satisfaction. Therefore, it deserves a prominent place in any comparison of whey isolate vs concentrate. It empowers consumers to make informed decisions based on their individual needs and sensitivities, ensuring they can reap the benefits of whey protein without digestive distress.
4. Processing Methods and Bioactive Compounds
A key differentiator between whey isolate and concentrate lies in their processing methods, which directly impacts their bioactive compound profile. This is a crucial consideration when choosing between the two, as these compounds can offer significant health benefits beyond just muscle protein synthesis. Understanding these differences helps you make an informed decision based on your individual health and fitness goals.
Whey concentrate undergoes basic filtration to remove larger milk solids, leaving a protein concentration of around 80%. This simpler process preserves a greater amount of naturally occurring bioactive compounds. These beneficial components include immunoglobulins, which support immune function; lactoferrin, with its iron-binding and antimicrobial properties; and glycomacropeptides (GMPs), which may play a role in satiety and gut health. Cold-processed concentrate takes this a step further by using lower temperatures during processing, which helps retain even more of the native protein structures and minimizes denaturation, potentially maximizing the benefits of these bioactive compounds.
Whey isolate, on the other hand, undergoes a more extensive filtration process. This includes microfiltration, ultrafiltration, ion-exchange, or cross-flow microfiltration. These methods effectively remove more fat and lactose, resulting in a higher protein concentration, typically 90% or more. However, this rigorous filtration also strips away many of the beneficial bioactive compounds and microfractions present in whey concentrate. While isolate boasts a purer protein source, the trade-off is a reduced presence of these potentially health-boosting components. For example, ion-exchange isolates, known for their extremely high protein content, often have the lowest levels of bioactive compounds.
Pros:
- Concentrate: Contains more immune-supporting compounds like immunoglobulins, lactoferrin, and GMPs. Cold-processed concentrate preserves more native protein structures and bioactive compounds.
Cons:
- Isolate: Loses some of the beneficial non-protein components during processing, including immunoglobulins and lactoferrin.
Examples:
-
Cold-processed concentrates like Promix or Legion Whey+ often advertise their preserved bioactive compounds as a key selling point.
-
Ion-exchange isolates typically have the highest protein content but the lowest levels of bioactive compounds.
Tips:
-
Consider whey concentrate if you're looking for general health benefits beyond just muscle building, as it retains more of the immune-supporting and other beneficial compounds.
-
Look for cold-processed or low-temperature processed whey, whether concentrate or isolate, to maximize the preservation of bioactive compounds. Learn more about Processing Methods and Bioactive Compounds
This aspect of whey protein deserves a place on this list because the choice between isolate and concentrate isn't just about protein purity. The presence or absence of bioactive compounds plays a significant role in the overall health benefits you can derive from your protein supplement. While isolate provides a purer protein source ideal for those with lactose intolerance or focusing solely on muscle protein synthesis, concentrate, particularly cold-processed varieties, offers a broader spectrum of potential health benefits thanks to its retained bioactive compounds. Understanding these differences empowers you to choose the best option aligned with your specific needs and goals, whether it's maximizing muscle growth, supporting immune function, or achieving overall wellness.
5. Price and Cost-Effectiveness
When comparing whey isolate vs. concentrate, price and cost-effectiveness are major factors for many consumers. Due to the extra processing involved in its production, whey protein isolate comes with a higher price tag than whey protein concentrate. This price difference, typically ranging from 20-50% more for an equivalent amount of isolate, makes concentrate a significantly more budget-friendly option, especially for those new to supplementation or working with limited funds. This factor alone secures its place on this list as a crucial consideration for anyone looking to incorporate whey protein into their routine.
The higher cost of isolate stems from the additional filtration processes required to remove more fat and lactose. This results in a purer protein product with higher protein content per serving. Concentrate, on the other hand, undergoes less processing, leading to a lower production cost and, subsequently, a lower price for the consumer. For example, a popular brand like Optimum Nutrition offers Gold Standard 100% Whey (a concentrate blend) for approximately $0.85-1.00 per serving, while their Platinum Hydrowhey (an isolate) can cost around $1.30-1.50 per serving. This clearly demonstrates the price gap between the two forms of whey protein.
Pros of Choosing Concentrate Based on Cost:
-
More protein per dollar: Concentrate provides significantly more protein for each dollar spent, making it an economical choice.
-
Adequate protein quality: For the majority of users, the protein quality of concentrate is more than sufficient to support muscle growth and recovery.
Cons of Choosing Isolate Based on Cost:
-
Prohibitive price: The premium price of isolate can be a barrier for budget-conscious consumers.
-
Significant cost difference for daily use: The price difference becomes especially pronounced when consuming whey protein daily over extended periods.
Tips for Smart Shopping:
-
Calculate cost per gram of protein: Don't just compare serving prices. Instead, calculate the cost per gram of protein to get a true sense of value. This will help you identify the most cost-effective option.
-
Consider a mixed approach: A practical strategy is to use concentrate for your everyday protein needs and reserve isolate for specific situations like cutting phases, when a lower calorie and carbohydrate intake is prioritized, or when optimal digestibility is crucial.
Budget-conscious fitness enthusiasts, college students, and beginners in fitness supplementation often gravitate towards whey protein concentrate as an entry point due to its affordability. Learn more about Price and Cost-Effectiveness. Understanding the cost implications of whey isolate vs. concentrate empowers consumers to make informed decisions that align with their fitness goals and budget. Whether you prioritize absolute purity or cost-effectiveness, weighing the price alongside the benefits will help you choose the best whey protein product for your individual needs.
6. Mixability and Taste
When it comes to protein powder, how easily it mixes and how good it tastes are major factors influencing your daily consumption. In the whey isolate vs concentrate debate, significant differences exist in both mixability and flavor profile. These differences stem from the processing methods used to produce each type of whey protein. Whey isolate undergoes more extensive filtration, removing more fat and lactose than concentrate. This affects both texture and taste.

Whey isolate typically mixes more easily, dissolving readily into liquids with minimal effort. Its lower fat and lactose content result in a thinner consistency and a cleaner, less milky taste. This makes it ideal for those who prefer a lighter flavor profile, especially when mixing with just water. On the other hand, whey concentrate has a thicker, creamier texture and a more pronounced milk-like flavor due to the higher presence of these components. This can be desirable for individuals who enjoy a richer, more traditional milkshake-like experience. However, the thicker consistency can sometimes make it more challenging to mix thoroughly, potentially leading to clumps.
Features:
-
Isolate: Dissolves more readily, cleaner taste, requires less vigorous mixing, produces less froth and foam.
-
Concentrate: Thicker, creamier texture with a more milk-like flavor.
Pros:
-
Isolate: Preferred for mixing with water, creates smoother shakes with less foam.
-
Concentrate: Can offer a richer, more satisfying flavor for some.
Cons:
-
Isolate: May have a slightly less sweet taste which some find less appealing.
-
Concentrate: Can be more challenging to mix thoroughly, stronger dairy flavor that some may find unpleasant.
Examples:
-
Transparent Labs 100% Grass-Fed Whey Isolate: Markets its superior mixability as a key feature, targeting those who value convenience and a clean taste.
-
Optimum Nutrition Gold Standard Whey (concentrate blend): Known for its good taste despite being a concentrate-based blend, demonstrating that careful formulation can overcome some of the typical taste challenges associated with concentrate.
Tips:
-
For Concentrate: Use a blender or shaker bottle with a wire ball for optimal mixing. Letting the mixture sit for 1-2 minutes after initial shaking can also help achieve a smoother texture.
-
For Isolate: A simple shaker bottle is usually sufficient, but a blender can further enhance smoothness if desired.
Why it Matters: Mixability and taste play a crucial role in adherence to a supplement regimen. A protein powder that's easy to mix and enjoyable to drink increases the likelihood of consistent consumption, supporting your fitness goals. This factor is particularly important for fitness enthusiasts who drink protein shakes on-the-go and prioritize convenience. Brands like Isopure have capitalized on this demand by focusing on readily-mixable isolate formulas.
This difference in mixability and taste is a key consideration when choosing between whey isolate vs concentrate. Your choice depends on individual preferences and priorities. If ease of mixing and a clean taste are paramount, whey isolate is likely the better option. If you prioritize a richer, creamier texture and enjoy a more pronounced milk-like flavor, whey concentrate might be more appealing.
Whey Isolate vs Concentrate: 6 Key Comparisons
Implementation Complexity 🔄 | More extensive filtration (micro-, ion-exchange) | Basic filtration process |
Resource Requirements 💡 | Higher production cost due to extra processing | Lower cost with simpler processing |
Expected Outcomes 📊 | ≥90% protein, minimal fat/lactose, cleaner taste | 70-80% protein, higher fat/lactose, creamier taste |
Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Low-carb/low-fat diets, lactose sensitivity, cutting phases | Cost-effective supplementation, bulking, general health benefits |
Key Advantages ⭐ | Higher protein content, easier digestion, better mixability | Contains bioactive compounds, immune support, cost-effective |
Price & Cost-Effectiveness ⚡ | More expensive (20-50% higher price) | More budget-friendly, better protein per dollar |
Making the Right Whey Protein Choice
Choosing between whey isolate vs concentrate isn't a one-size-fits-all decision. As we've explored, key differences in protein content, fat and carbohydrate levels, digestibility, processing, and price all contribute to making one form of whey protein more suitable for certain individuals over the other. Those prioritizing maximum protein purity, adhering to low-carb or low-fat diets, or experiencing lactose sensitivity will likely find whey isolate to be the better choice. On the other hand, whey concentrate provides a more budget-friendly option, often with the added benefit of naturally occurring bioactive compounds. Understanding these nuances empowers you to make informed decisions about your supplementation, optimizing your results and supporting your overall health and fitness journey.
Mastering the distinctions between whey isolate vs concentrate is crucial for anyone serious about maximizing the benefits of protein supplementation. Whether you're a seasoned bodybuilder, a health-conscious consumer, or simply looking to improve your dietary intake, understanding these differences allows you to tailor your supplement choices to your specific needs and goals, ultimately contributing to improved physical performance, better recovery, and enhanced overall well-being.
Ready to make the best choice for your body and budget? Visit WheyIndex to easily compare whey protein products side-by-side. WheyIndex helps you analyze ingredients, assess value, and navigate the complexities of whey isolate vs concentrate, so you can confidently find your perfect protein match.
.png)




